- About Us
- Conditions We Treat
- Services
- Diagnostic Testing
- Infection Control
- Skin Substitutes
- Arobella The Qoustic Wound Therapy System
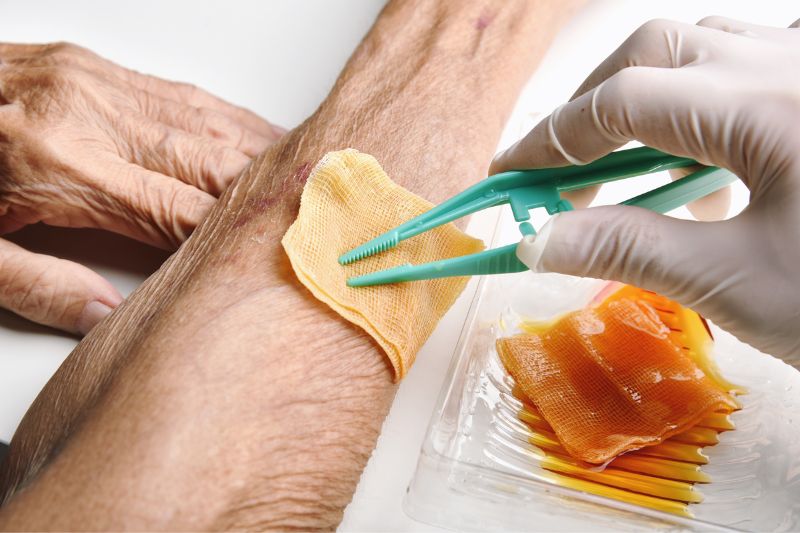
- Wound Debridement
- Education and Prevention
- Pressure-Relieving Devices
- Incision and Drainage
- Specialized Dressing and Topical Applications
- Compression Therapy / Multi-Layer Compression Wraps
- Nutritional Evaluation and Counseling
- New Patients
- Contact Us
close
- About Us
- Conditions We Treat
- Services
- Diagnostic Testing
- Infection Control
- Skin Substitutes
- Arobella The Qoustic Wound Therapy System
- Wound Debridement
- Education and Prevention
- Pressure-Relieving Devices
- Incision and Drainage
- Specialized Dressing and Topical Applications
- Compression Therapy / Multi-Layer Compression Wraps
- Nutritional Evaluation and Counseling
- New Patients
- Contact Us
Menu
- About Us
- Conditions We Treat
- Services
- Diagnostic Testing
- Infection Control
- Skin Substitutes
- Arobella The Qoustic Wound Therapy System
- Wound Debridement
- Education and Prevention
- Pressure-Relieving Devices
- Incision and Drainage
- Specialized Dressing and Topical Applications
- Compression Therapy / Multi-Layer Compression Wraps
- Nutritional Evaluation and Counseling
- New Patients
- Contact Us
close